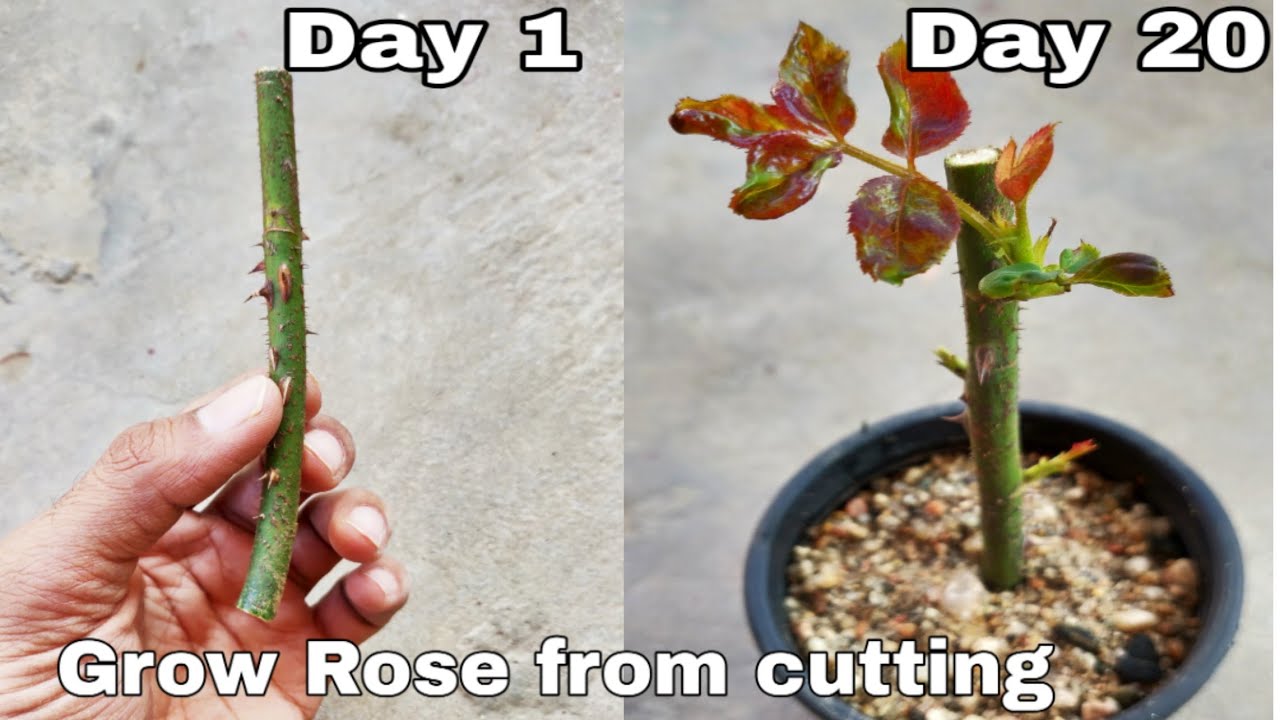
Grow Roses Like a Pro: How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings for Newbies sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Transform your garden into a vibrant rose haven by mastering the art of rose propagation from cuttings.
This guide will walk you through the process, from selecting the right cuttings to nurturing them into thriving new plants.
Imagine the satisfaction of watching a tiny rose cutting transform into a magnificent, blooming rose bush. Propagating roses from cuttings is not only a rewarding experience, but it’s also a cost-effective way to expand your rose collection and share the beauty with friends and family.
By following these simple steps, even novice gardeners can achieve success and enjoy the wonders of growing their own roses.
Introduction: Grow Roses Like A Pro: How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings For Newbies
Rose propagation is a rewarding and fulfilling gardening endeavor. The joy of creating new rose plants from cuttings is unmatched. Not only does it save money, but it also allows you to expand your rose collection with your favorite varieties.
Advantages of Rose Propagation
Rose propagation from cuttings offers numerous benefits over purchasing new plants from nurseries. Here are some key advantages:
- Cost-effectiveness:Propagating roses from cuttings is significantly cheaper than buying new plants. You can create multiple new roses from just one parent plant, making it a very economical way to expand your rose garden.
- Genetic Diversity:Rose propagation from cuttings allows you to preserve the unique characteristics of your existing roses, ensuring that you can enjoy the same beautiful blooms and fragrance in your new plants. This is particularly important for rare or heirloom rose varieties that may not be readily available for purchase.
- Personal Satisfaction:There is a sense of accomplishment and satisfaction that comes with successfully propagating roses from cuttings. It’s a rewarding experience that deepens your connection with your garden and your plants.
Choosing the Right Cuttings
Taking cuttings from the right rose stems is crucial for successful propagation. The quality of your cuttings directly impacts their ability to root and thrive.
Timing is Key: The Ideal Time for Rose Cuttings
The best time to take rose cuttings is during the dormant season, typically in late fall or early winter. This period offers several advantages:
- Reduced Sap Flow:During dormancy, rose stems have reduced sap flow, making them less prone to wilting and more likely to root successfully.
- Lower Risk of Disease:The cooler temperatures and reduced moisture during dormancy minimize the risk of fungal infections and other diseases.
- Increased Success Rate:Studies have shown that rose cuttings taken during dormancy have a higher success rate than those taken during the growing season.
Selecting Healthy Rose Stems
Choosing healthy, disease-free rose stems is essential for successful propagation. Here’s how to select the right stems:
- Look for Stems from Healthy Roses:Avoid taking cuttings from roses that are showing signs of disease, pests, or stress. Look for vigorous, healthy plants with lush foliage.
- Choose Stems with New Growth:Select stems from the current year’s growth, as they are more likely to root successfully. These stems are typically more flexible and have a lighter green color.
- Avoid Stems with Flowers or Buds:Cuttings taken from stems with flowers or buds will divert energy to these structures, reducing the energy available for rooting.
Ideal Characteristics of a Good Rose Cutting
The ideal rose cutting has specific characteristics that increase its chances of rooting:
- Stem Thickness:The stem should be about the thickness of a pencil, or approximately 1/4 inch in diameter. This provides a balance between strength and flexibility.
- Leaf Nodes:Each cutting should have at least two or three leaf nodes. Leaf nodes are the points on the stem where leaves grow, and they contain dormant buds that can develop into roots.
- Bud Presence:Choose stems with at least one bud located just below the top leaf node. This bud will develop into a new shoot, contributing to the cutting’s growth.
Preparing the Cuttings
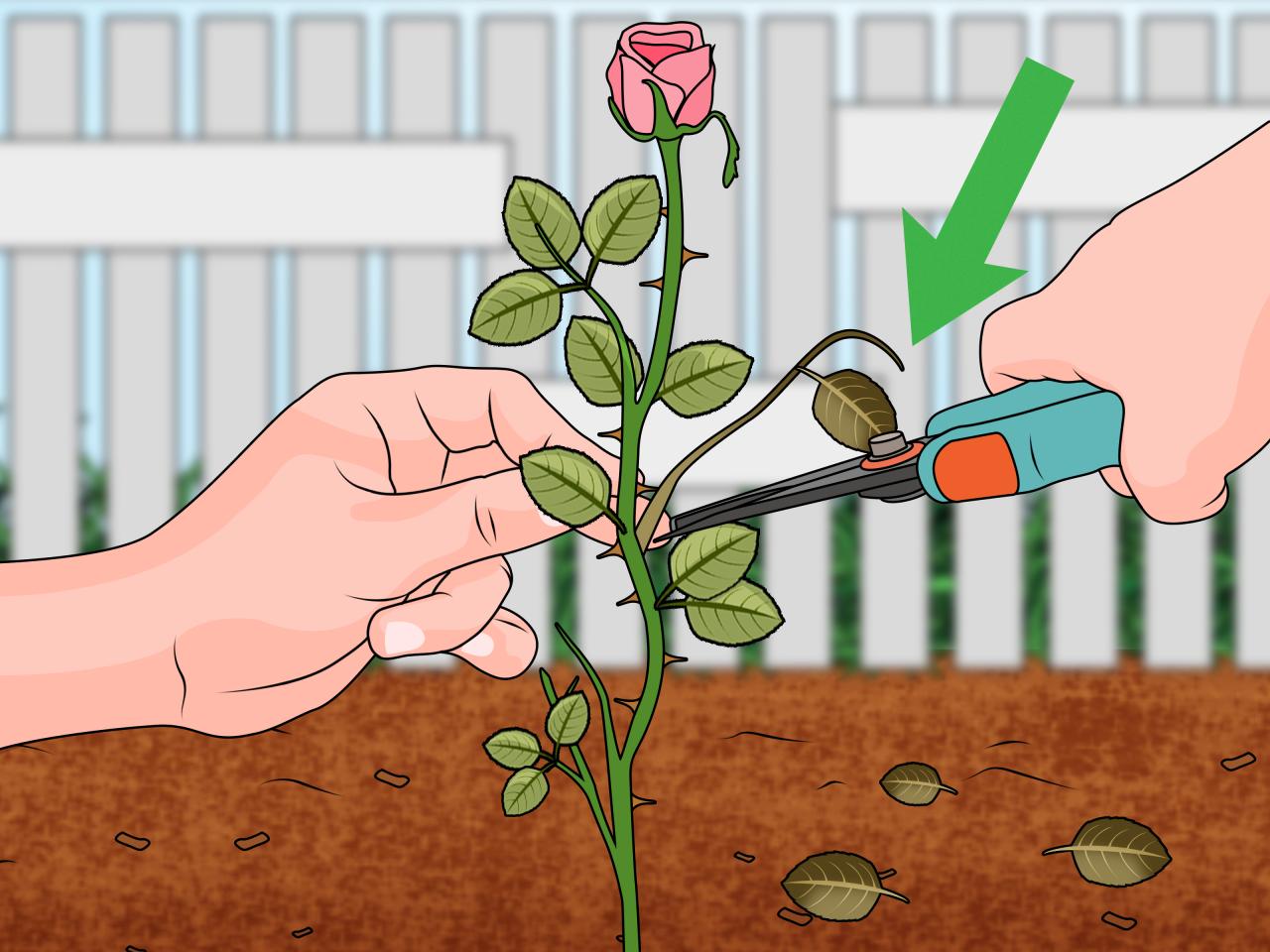
Now that you’ve selected the perfect rose cuttings, it’s time to prepare them for rooting. This involves making precise cuts and removing unnecessary leaves to maximize their chances of success.
Making the Cuts
Using sharp, clean tools is essential for preparing rose cuttings. Dull tools can crush the stem, increasing the risk of infection and hindering root development. Here’s how to make the cuts:
- Cut at a 45-degree angle:This angled cut provides a larger surface area for root growth.
- Cut just below a node:Nodes are the points on the stem where leaves emerge. They contain dormant buds that can develop into roots.
- Remove any leaves below the cut:These leaves will draw energy from the cutting and hinder root development.
Treating the Cuttings
Once the cuttings are prepared, you can treat them with rooting hormone or a rooting solution to boost their chances of rooting.
- Rooting hormone:This powder or liquid contains plant hormones that stimulate root growth. Apply a small amount to the cut end of the cutting before planting.
- Rooting solution:These solutions contain a mix of nutrients and hormones that promote root development. Soak the cuttings in the solution for a few hours before planting.
Planting and Rooting
Once your rose cuttings are prepped, it’s time to create a suitable environment for them to root. This involves choosing the right rooting medium, employing appropriate planting methods, and ensuring optimal humidity and temperature conditions.
Choosing the Right Rooting Medium
The rooting medium provides essential support and nutrients for your rose cuttings as they develop roots. There are several popular options, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
- Potting Mix:This is a widely available and cost-effective option, often consisting of a blend of peat moss, vermiculite, and perlite. It provides good drainage and aeration, essential for healthy root development. However, it can sometimes become compacted, requiring careful watering to avoid over-saturation.
- Vermiculite:This lightweight, sterile material retains moisture well, making it ideal for rooting cuttings. It provides good aeration and is less prone to compaction than potting mix. However, it may require more frequent watering to maintain optimal moisture levels.
- Perlite:This lightweight, volcanic glass material provides excellent drainage and aeration. It’s often used in combination with other rooting mediums, like potting mix or vermiculite, to improve their drainage and prevent compaction. Perlite doesn’t retain moisture as well as vermiculite, so careful monitoring and watering are crucial.
Planting Methods
There are two primary methods for planting rose cuttings:
- Direct Planting in Pots:This method involves planting cuttings directly into individual pots filled with the chosen rooting medium. It offers flexibility and allows you to monitor each cutting’s progress closely. Fill the pots with your chosen rooting medium, leaving a small space at the top for watering.
Make a hole in the center of the medium, slightly deeper than the length of the cutting. Dip the cut end of the cutting in rooting hormone and gently insert it into the hole. Firm the medium around the cutting to ensure stability.
- Using Propagation Trays:These trays are designed with individual cells or compartments to hold cuttings. They provide a controlled environment and are especially useful for large-scale propagation. Fill the trays with your chosen rooting medium, leaving a small space at the top for watering.
Make a hole in the center of each cell, slightly deeper than the length of the cutting. Dip the cut end of the cutting in rooting hormone and gently insert it into the hole. Firm the medium around the cutting to ensure stability.
Humidity and Temperature
Creating a humid environment is crucial for successful rooting. This is because cuttings need moisture to initiate root growth.
Humidity:Maintaining high humidity levels is essential for successful rooting. This can be achieved by covering the cuttings with a plastic dome, a clear plastic bag, or a humidity tent. The dome or bag traps moisture around the cuttings, creating a warm, humid environment that promotes root development.
Growing roses from cuttings is a rewarding and affordable way to expand your rose garden. While the process is simple, there are a few key steps to ensure success. One important aspect is choosing the right cutting material – similar to how selecting the best stems is crucial when propagating clematis, as outlined in this helpful guide How to Make Clematis Propagation Easy and Effective.
Once you’ve got your cuttings, you’ll need to prepare them for rooting, a process that involves removing leaves and making a clean cut. With a little patience and care, you’ll soon be enjoying the beauty of your own rose bushes.
Temperature:Most rose cuttings root best in temperatures between 70-75 degrees Fahrenheit (21-24 degrees Celsius). This warm environment encourages root growth and prevents the cuttings from becoming stressed. You can achieve this temperature by placing the cuttings in a warm location, using a heating mat, or placing them under a grow light.
Caring for Your Cuttings
You’ve successfully planted your rose cuttings, and now it’s time to provide them with the care they need to develop strong roots and flourish. Consistent care, including proper watering, protection from pests and diseases, and adequate light, will significantly impact your success in propagating roses.
Propagating roses from cuttings is a rewarding and cost-effective way to expand your rose garden. Similar to roses, schefflera plants can also be easily propagated from cuttings, offering a simple and successful method to create new plants. For a comprehensive guide on growing new schefflera plants from cuttings, check out The Complete Guide to Growing New Schefflera Plants from Cuttings.
With a little patience and the right techniques, you’ll soon be enjoying a flourishing collection of roses and schefflera plants.
Watering Rose Cuttings
Watering is crucial for the rooting process, as it helps keep the soil moist and encourages root development. However, overwatering can lead to root rot, so finding the right balance is key.
- Water deeply and infrequently:Instead of frequent, shallow watering, water your cuttings thoroughly but less often. Allow the top inch of soil to dry out between waterings. This encourages roots to grow deeper in search of moisture.
- Use a watering can with a fine rose:This helps distribute water evenly and avoids disturbing the cuttings.
- Avoid getting water on the leaves:Wet leaves can increase the risk of fungal diseases.
- Monitor the soil moisture:Stick your finger into the soil to check for moisture levels. If it feels dry, it’s time to water.
Protecting Rose Cuttings from Pests and Diseases
Rose cuttings are susceptible to pests and diseases, particularly in humid environments. Taking preventative measures can help protect your cuttings and ensure their healthy growth.
- Use a fungicide:Applying a fungicide to the soil and cuttings can help prevent fungal infections. Follow the instructions on the product label carefully.
- Inspect cuttings regularly:Look for signs of pests or diseases, such as aphids, spider mites, or powdery mildew.
- Isolate infected cuttings:If you notice signs of pests or diseases, isolate the infected cuttings to prevent spreading to healthy ones.
Providing Adequate Light
Rose cuttings need sufficient light for photosynthesis and healthy growth, but direct sunlight can scorch their delicate leaves.
- Bright, indirect light:Place your cuttings in a location with bright, indirect light, such as a windowsill with a sheer curtain or a shaded area outdoors.
- Avoid direct sunlight:Direct sunlight can burn the leaves and hinder rooting.
- Rotate the cuttings:Rotate the cuttings regularly to ensure all sides receive adequate light.
Transplanting and Establishing
After weeks of diligent care, your rose cuttings are ready for their next stage: transplanting. This crucial step marks the transition from a delicate seedling to a thriving rose plant. Successful transplanting ensures your cuttings have the space and resources to flourish and eventually produce beautiful blooms.
Signs of Successful Rooting
Before transplanting, it’s essential to confirm that your rose cuttings have successfully rooted. Several signs indicate a healthy root system:
- New growth:The appearance of new leaves and shoots signifies that the cutting is drawing nutrients and water from the soil through its newly developed roots.
- Firmness:Gently tug on the cutting. If it offers resistance, it’s a good indication that roots have anchored it firmly in the soil.
- Root development:If you’re using a clear container, you might be able to see white root hairs emerging from the base of the cutting.
If you observe these signs, your rose cuttings are ready for transplanting.
Transplanting Rooted Rose Cuttings
Once your cuttings have successfully rooted, you can transplant them into larger pots or directly into your garden. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Prepare the new container:Choose a pot that’s slightly larger than the original container. Fill it with fresh, well-draining potting mix. If planting directly into the garden, ensure the soil is well-prepared and amended with compost or other organic matter.
- Gently remove the cutting:Carefully loosen the cutting from its original container by gently tapping the sides. If it’s stuck, you can use a small trowel or garden fork to help dislodge it.
- Inspect the roots:Examine the root system. If it’s tightly packed, gently tease the roots apart to encourage them to spread out in the new container.
- Plant the cutting:Create a hole in the new container or garden bed that’s the same depth as the original container. Place the cutting in the hole, ensuring the root ball is completely covered with soil.
- Firmly pack the soil:Gently pat down the soil around the cutting to ensure good contact with the roots.
- Water thoroughly:After transplanting, water the cutting deeply to settle the soil and hydrate the roots.
Hardening Off Rose Cuttings
Before planting your rooted cuttings directly into the garden, it’s essential to harden them off. Hardening off gradually acclimates your cuttings to the outdoor environment, reducing the risk of shock and ensuring their survival. Here’s how:
- Start with shade:Begin by placing your cuttings in a sheltered, shaded area for a few hours each day. This will gradually introduce them to the sun and wind.
- Increase exposure:Over the next week or two, gradually increase the amount of time your cuttings spend in the sun, extending the exposure by a few hours each day.
- Monitor for signs of stress:Observe your cuttings for signs of stress, such as wilting or scorching. If you notice any signs, reduce the exposure time or move them back to a shaded location.
- Plant in the garden:Once your cuttings have acclimated to the outdoor environment, you can safely plant them in your garden.
Troubleshooting
Even with the best care, rose cuttings can encounter problems during propagation. It’s crucial to monitor them regularly for signs of stress or disease. Early detection and intervention can significantly improve your success rate. This section addresses common challenges and provides solutions to help you overcome them.
Stem Rot
Stem rot is a common problem in rose propagation, often caused by excessive moisture or poor drainage. The base of the cutting may turn soft, mushy, and discolored, indicating decay.
- Preventative Measures:
- Use a well-draining potting mix.
- Avoid overwatering.
- Ensure good air circulation around the cuttings.
- Treatment:
- If you notice stem rot, remove the affected cutting immediately.
- Disinfect your tools to prevent spreading the infection.
- Repot the remaining cuttings in fresh, sterile potting mix.
Fungal Infections, Grow Roses Like a Pro: How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings for Newbies
Fungal infections can affect rose cuttings, causing leaf spots, powdery mildew, or black spot. These infections thrive in humid conditions and can spread rapidly.
- Preventative Measures:
- Use clean tools and potting mix.
- Avoid overcrowding cuttings.
- Provide good air circulation.
- Water cuttings in the morning to allow foliage to dry quickly.
- Treatment:
- Remove and discard any infected leaves or stems.
- Apply a fungicide specifically designed for roses.
- Improve air circulation around the cuttings.
Slow Rooting
Rose cuttings may take several weeks or even months to root. Slow rooting can be caused by factors such as poor cutting selection, improper rooting conditions, or environmental stress.
- Preventative Measures:
- Choose healthy, vigorous cuttings.
- Ensure proper rooting conditions, including adequate moisture, temperature, and humidity.
- Protect cuttings from extreme temperatures and direct sunlight.
- Treatment:
- Check the rooting medium for moisture levels.
- Consider using a rooting hormone to stimulate root development.
- Monitor the cuttings for signs of new growth, which indicates successful rooting.
Success Stories and Tips

The journey from newbie to pro rose propagator is filled with rewarding experiences. Many rose enthusiasts have found success in this rewarding endeavor, and their stories are a testament to the power of patience, persistence, and a little bit of rose magic.
Inspiring Success Stories
Successful rose propagation is often a testament to the dedication and patience of the grower. Here are some inspiring stories that highlight the journey from newbie to pro:
- A first-time rose propagator, inspired by a friend’s success, successfully rooted several cuttings from a beloved heirloom rose bush. The satisfaction of seeing new life emerge from a simple cutting was a truly rewarding experience.
- A novice gardener, armed with a newfound knowledge of rose propagation techniques, successfully rooted a challenging variety known for its difficult propagation. This accomplishment boosted their confidence and sparked a passion for cultivating unique and rare rose varieties.
Tips for Optimizing Success
Rose propagation is a rewarding journey, but it’s also an ongoing learning process. Here are some additional tips to help you optimize your success:
- Experiment with different propagation methods.There are several techniques, such as air layering and grafting, that can be explored to discover what works best for your specific rose varieties and climate.
- Maintain a consistent environment.Rose cuttings thrive in warm, humid conditions. Use a propagation mat or heat source to maintain the ideal temperature, and mist regularly to prevent drying.
- Choose the right time of year.The best time to propagate roses is during the spring or early summer when the plant is actively growing.
- Don’t give up too soon.Rose propagation can take time. Be patient and persistent, and don’t be discouraged if your first attempt isn’t successful. With practice and experimentation, you’ll eventually find what works best for you.
The Joy of Cultivating New Rose Plants
The journey from newbie to pro rose propagator is not just about the technical skills, but also about the joy of nurturing new life and creating a personal connection with your roses. The satisfaction of seeing a tiny cutting transform into a thriving rose plant is a truly rewarding experience.
The process of propagation also fosters a deeper appreciation for the beauty and resilience of these remarkable plants.
Ultimate Conclusion
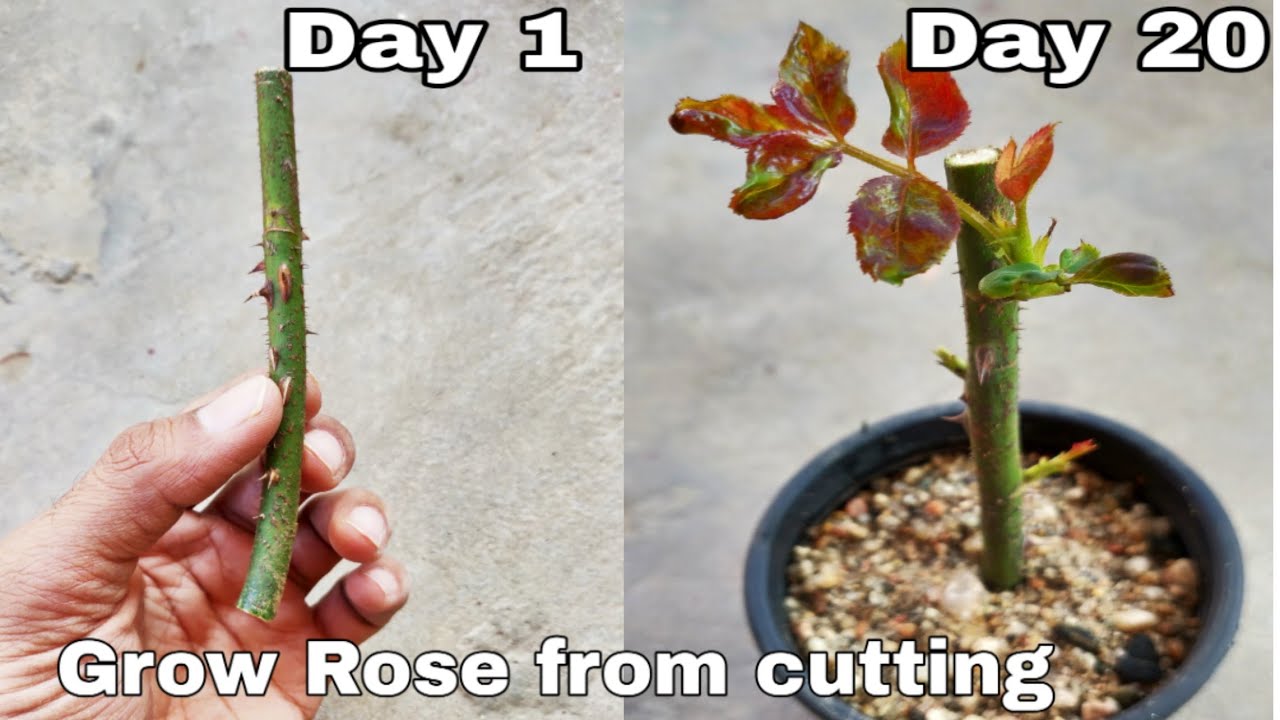

With a little patience and care, you can easily propagate your own roses from cuttings, adding vibrant color and fragrance to your garden. The joy of watching your new rose bushes flourish is a testament to your gardening skills and a testament to the magic of plant propagation.
So, grab your pruning shears, gather some cuttings, and embark on this rewarding journey of creating a rose haven in your own backyard. Remember, the journey of a thousand roses begins with a single cutting.
FAQ Summary
What are the best types of roses to propagate from cuttings?
Most rose varieties can be propagated from cuttings, but hybrid teas and floribunda roses are known for their success rate.
Can I propagate roses from store-bought roses?
Yes, you can! Choose healthy stems from roses purchased from a nursery or florist.
How long does it take for rose cuttings to root?
Rooting time can vary depending on the rose variety and environmental conditions, but it typically takes 4-6 weeks.
What should I do if my rose cuttings don’t root?
Don’t despair! Try adjusting the rooting environment, ensuring proper humidity and temperature. You can also try using a different rooting hormone.
